Introduction
Visual is an event driven language which has some features of Object Oriented Programming (OOP). Actions are tied to the occurrence of events e.g. an action may be triggered by clicking the mouse. This approach make application programs more friendly and natural to the end user. In this unit students are introduced to the concept of working with graphical objects and the general Visual Basic Programming concepts.MUST READ:A
- computer hardware
- computer application programming using visual basic
- areas of application of computers
- auxillary equipment
- assembling the entire system-computer
- basic principles of computer programming
- cd rom failure – symptoms and troubleshooting
- classification of computers
- computer applications in government, science, engineering, transport, communications, recreation and the military
- computer applications in the bunesss and industry
- computer languages
- checking the power supply
Learning To Run Visual Basic Applications
These sessions will include learning how to work with graphical objects in the Visual Basic Environment and using general Visual Basic Programming concepts. How To Design A Project From The Application Wizard.A project is a collection of files that make up your application. A single application might consist of several files, and the project is the collection of those files.
The application wizard can be selected from the New Project dialog box. If you cancel the New Project dialog box, and then later want to start the Application wizard, select File, New Project to display the New Project dialog box once again. The screen you see looks like that in Figure 1.
Figure 1
When you select the icon labeled VB Application Wizard on the New tab, the wizard begins its work. The interface type you select will determine how your application will process multiple windows. See figure 2.
Figure 2
Figure 3
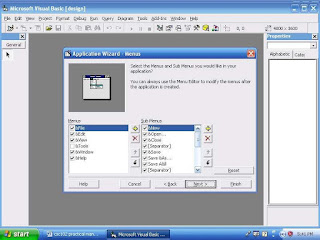
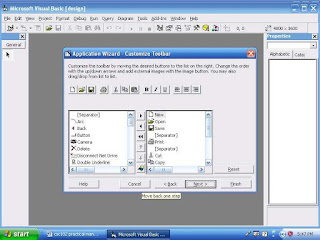
You can select the options you want your application’s menu to contain as shown in Figure 3 above. The options are common Windows options found on most Windows programs. The ampersand (&) next to a letter in a menu name indicates the underscored accelerator key letter; in other words, &New indicates that New appears on the menu and that the use can select the option by pressing Alt+N. The next wizard screen, shown in Figure 4, lets you select the toolbar buttons that your application will have. Click next to accept all the default toolbar settings.
Splash screen is an opening title screen that appears when your application first begins.
- Login dialog is a dialog box that asks for the user’s ID and password as a part of
- application security that you can add.
- • Options dialog is tabbed blank dialog box from which your users can specify
- attributes that you set up for the application.
- • About box is a dialog box that appears when your users select Help, About from the application menu.
- You can also select a form template from here. A form template is model of a form that you can customize.
- Click Next to get to the last screen and click the Button labeled Finish to instruct Visual Basic to complete your initial application.
How To Create A Project From The New Project Window
The New Project window appears, when you first start Visual Basic or when you select File, New Project. You will always need toolbars in your project. Visual Basic has a total of four toolbars:•Debug. This toolbar appears when you use the interactive debugging tools to trace and correct problems.
• Edit. This toolbar aids your editing of Visual Basic code.
• Form Editor. This toolbar helps you adjust objects on forms.
Standard. This toolbar is the default toolbar that appears beneath the menu bar.
You can display and hide these toolbars from the View, Toolbars menu.
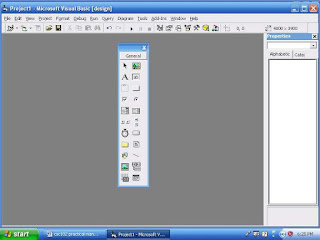
Using the Toolbox
The Toolbox window differs from the toolbar. The toolbox is a collection of tools that act as a repository of controls you can place on a form. Figure 5 shows the most common collection of toolbox tools that you’ll see.
Figure 5




Social Plugin